carothers equation polymer
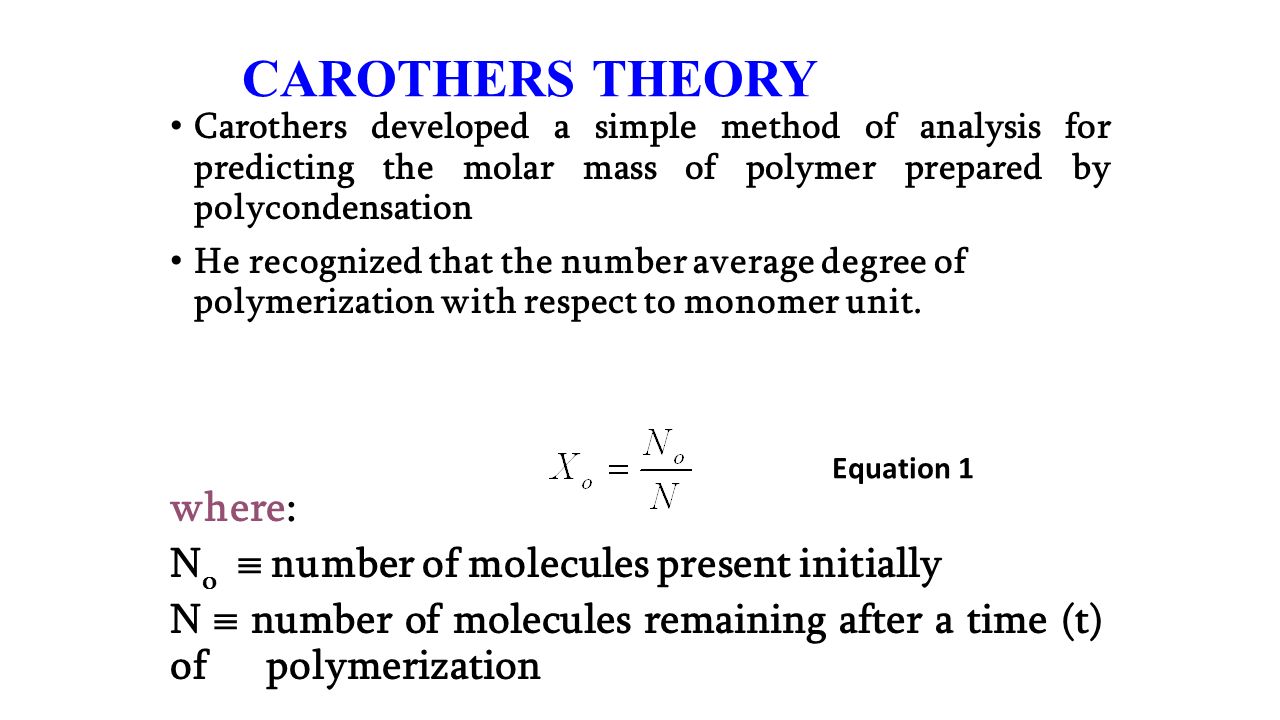
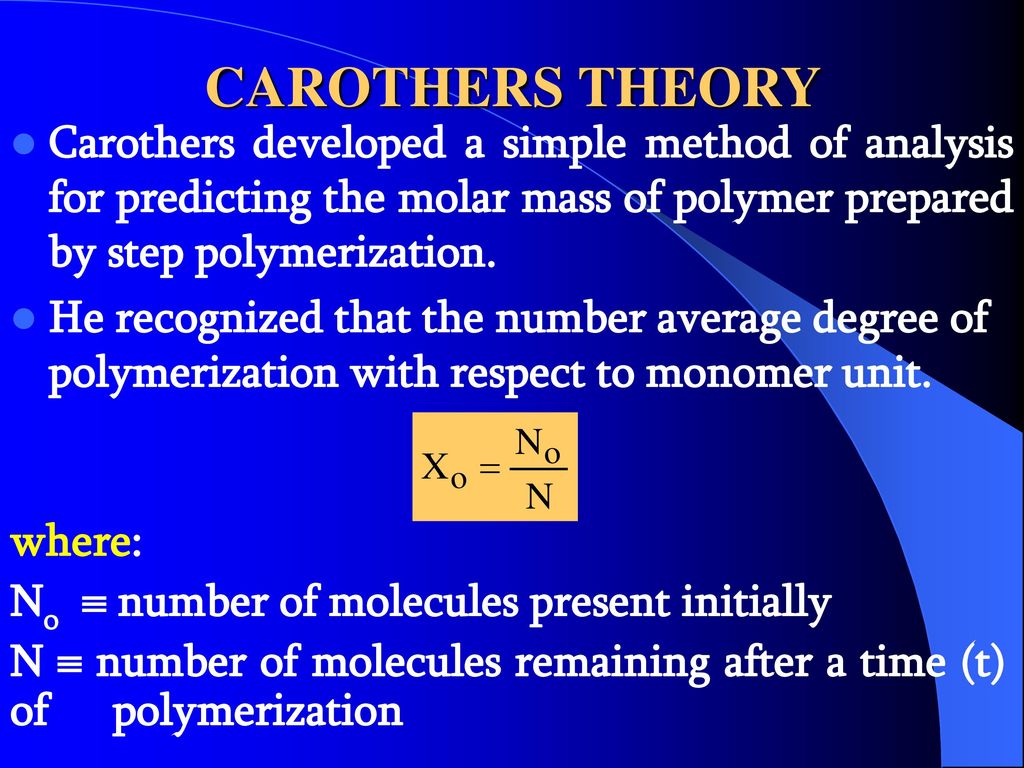
The basic assumptions involved in deriving the Carothers equation are reviewed in this section. I A major assumption is that the reactivity of all functional groups of the same kind is equivalent and independent of the size of the molecule to which the functional group is attached.
Degree Of Polymerization Dp Ppt Video Online Download
Popular works include Controlling Molecular Weight of a High Efficiency DonorAcceptor Conjugated Polymer and Understanding Its Significant Impact on Photovoltaic Properties Hydrogenbonded supramolecular polyether.

. This equation was proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. And the modified Carothers equation is 4 5 6 where p equals to Related equations. Number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule.
One monomer in excess. P is the extent of reaction or conversion to polymer defined by p N 0 NN 0 where N 0 is the number of molecules present initially and N is the. Carothers equation is applicable only to stoichiometric mixtures of addition monomers or if only one type of functional group undergoes polymerization as it is the case with chain growth.
There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. X n is also the average chain length in monomer units p N 0-NN 0 where. There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935.
The theory was initially conceptualized by Paul Flory in 1941 and then was further developed by. Thus the second term of the Carother equation vanishes and the critical extent of the reaction p c is given by. In the last stages of polymerization the rate of polymerization will be low because the concentration of.
Step-growth polymerization vs chain growth to be covered in more detail later in the course extent of reaction number-average degree of polymerization. Carothers equation and Monomer See more Nylon. Measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture.
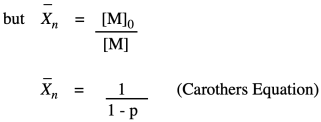
In this equation X n is the number-average value of the degree of polymerization equal to the average number of monomer units in a polymer molecule. Derivation of the Carothers equation for molecular mass as a function of the extent of the reaction p and reactant ratio r. In polycondensations the number-average degree of polymer- ization DP can be expressed as DP 1 r1 r 2rp where p is the extent of the polymerization and r is the stoichiometric ratio between the comonomers.
The simplest case refers to the formation of a strictly. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p. Two monomers in equimolar quantities.
There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. Carothers equation is an research topic. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p.
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers based on aliphatic or semi-aromatic polyamides. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p. The Carothers equation is often used to predict the utility of a small molecule reaction in a polymerization.
Nylon 66 nylon 6-6 nylon 66 or nylon 66 is a type of polyamide or nylon. This equation was originally proposed by Carothers and is often referred to as. P c 2 f avg.
An equation attributed to Carothers 1 relates the number-average degree of polymerization to fractional monomer-conversion p in a step-growth polymerization as see Example Problem 12 X n 1 1 p. Derivation of the Carothers. X w is the weight average degree of polymerization M n is the number average molecular weight.
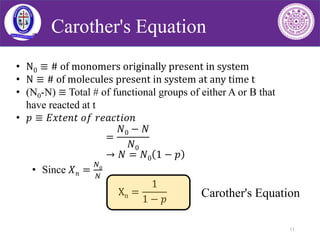
N 0 is the number of molecules present initially N is the number of unreacted molecules at time t p is also a measure of the extent of reaction or yield. Xn a high fractional monomer conversion p is required according to Carothers equation For example a monomer conversion of p 99 would be required to achieve Xn 100. The Carothers Equation High Molecular weights are hard to get this way If there are N omolecules at time 0 and N remaining at time t then the amount reacted is N 0 -N and we can define p as the conversion or fraction reacted then as P N o N N o or N N o 1 P If DP is the average degree of polymerization N 0.
There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935. In this study we present the mechanistic. 21 Similarly the weight-average degree of.
FloryStockmayer theory is a theory governing the cross-linking and gelation of step-growth polymers. Carothers equation In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization Xn for a given fractional monomer conversion p. In step-growth polymerization the Carothers equation or Carothers equation gives the degree of polymerization X n for a given fractional monomer conversion p.
Carothers equation and Nylon See more Nylon 66. For the example of nylon-66 where X n 2n n diamine units and n diacid units. Carothers equation and Nylon 66.
Related to the Carothers equation are the following equations for the simplest case of linear polymers formed from two monomers in equimolar quantities. Two monomers in equimolar quantities. Two monomers in equimolar quantities.
The American Chemical Society designated Wallace Carothers contributions to modern polymer science and the development of nylon as National Historic Chemical Landmarks in ceremonies on October 26 1995 at the DuPont nylon plant now operated by Invista in Seaford Delaware and on November 17 2000 at the DuPont Experimental Station in. In the case of non-stoichiometric ratios of two or more different. There are several versions of this equation proposed by Wallace Carothers who invented nylon in 1935.
One monomer in excess. Over the lifetime 13 publications have been published within this topic receiving 355 citations. The Flory-Stockmayer theory represents an advancement from the Carothers equation allowing for the identification of the gel point for polymer synthesis not at stoichiometric balance.

Degree Of Polymerization Of Polymers Materials Today

Lecture 2 The Carothers Equation Youtube

Degree Of Polymerization Of Polymers Materials Today

Spring 2007 Chap 8 Polycondensation Reactions Classification By
3 2 Kinetics Of Step Growth Polymerization Chemistry Libretexts
Carothers Theory Carothers Developed A Simple Method Of Analysis For Predicting The Molar Mass Of Polymer Prepared By Step Polymerization He Recognized Ppt Download

Introduction To Polymers Lecture 5 5 Step Growth Molecular Weight Part 2 Youtube
Chapter 9 Kinetics Of Chain And Step Growth Polymerization

Part5 Step Growth Polymerization Youtube

Introduction To Polymers Lecture 5 4 Step Growth Molecular Weight Part 1 Youtube

Spring 2007 Chap 8 Polycondensation Reactions Classification By
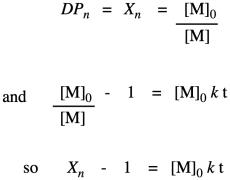
3 2 Kinetics Of Step Growth Polymerization Chemistry Libretexts

Carothers Theory L Carothers Developed A Simple Method

Carothers Theory Carothers Developed A Simple Method Of Analysis For Predicting The Molar Mass Of Polymer Prepared By Step Polymerization He Recognized Ppt Download

Spring 2007 Chap 8 Polycondensation Reactions Classification By

Dodt Oxidative Polymerization Data Dashed Line Plotted Against The Download Scientific Diagram

Macromolecular Chemistry Lecture 5 Step Growth Chain Growth

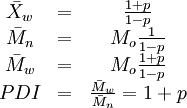
0 Response to "carothers equation polymer"
Post a Comment